Mathématiques 1re Techno
Rejoignez la communauté !
Co-construisez les ressources dont vous avez besoin et partagez votre expertise pédagogique.
Mes Pages
Partie 1 : Analyse
Ch. 1
Suites
Ch. 2
Fonctions
Ch. 3
Dérivation
Partie 2 : Statistiques et probabilités
Ch. 4
Fréquences conditionnelles et probabilités conditionnelles
Ch. 5
Variables aléatoires
Automatismes
Partie 3 : Géométrie
Ch. 6
Trigonométrie
Ch. 7
Produit scalaire
Ch. 8
Nombres complexes
Partie 4 : Analyse
Ch. 9
Compléments sur la dérivation
Ch. 10
Primitives
Révisions Genially
Chapitre 7
TP Info
Annuler le travail d'une force
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Énoncé
Le travail \text{W}, exprimé en joule, d'une force \overrightarrow{\text{F}}, en newton, sur un déplacement rectiligne \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}, en mètre, est défini par \text{W}=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}} \cdot \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}.
Dans un repère orthonormé, on considère trois points \mathrm{A}(1 \: ; 16), \mathrm{B}(-7 \: ; 18) et \mathrm{F}_{n}\left(n \: ; n^{2}-20\right), où n désigne un entier naturel.
Dans un repère orthonormé, on considère trois points \mathrm{A}(1 \: ; 16), \mathrm{B}(-7 \: ; 18) et \mathrm{F}_{n}\left(n \: ; n^{2}-20\right), où n désigne un entier naturel.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
On souhaite déterminer la valeur de \bm{n} pour laquelle le travail de la force \overrightarrow{\mathbf{AF}_{\bm{n}}} lors du déplacement \overrightarrow{\mathbf{AB}} est nul, en utilisant une des trois méthodes.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Méthode de résolution 1 Python
1. Calculer les coordonnées de \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}, puis exprimer les coordonnées de \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AF}_{n}} en fonction de n.
2. En déduire que \mathrm{W}=2 n^{2}-8 n-64.
3. Voici ci‑dessous un programme écrit en langage Python.
a. Justifier la ligne 3 du programme.
b. Que doit‑on saisir en lignes 4 et 6 pour que cet algorithme affiche la valeur de n pour laquelle \text{W} est nul ?
c. À quoi correspond la valeur y affichée en fin d'algorithme ?
4. Saisir et lancer cet algorithme. Donner la valeur de n telle que le travail soit nul, puis donner les coordonnées de \mathrm{F}_{n} correspondantes.
2. En déduire que \mathrm{W}=2 n^{2}-8 n-64.
3. Voici ci‑dessous un programme écrit en langage Python.
from math import* n = 0 p = -64 while ... : n = n + 1 p = ... y = n**2 - 20 print(n) print(y)
a. Justifier la ligne 3 du programme.
b. Que doit‑on saisir en lignes 4 et 6 pour que cet algorithme affiche la valeur de n pour laquelle \text{W} est nul ?
c. À quoi correspond la valeur y affichée en fin d'algorithme ?
4. Saisir et lancer cet algorithme. Donner la valeur de n telle que le travail soit nul, puis donner les coordonnées de \mathrm{F}_{n} correspondantes.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Méthode de résolution 2 Tableur
1. Reproduire la feuille de calcul suivante et compléter les cellules \bf{B1}, \bf{B2}, \bf{D1} et \bf{D2}.

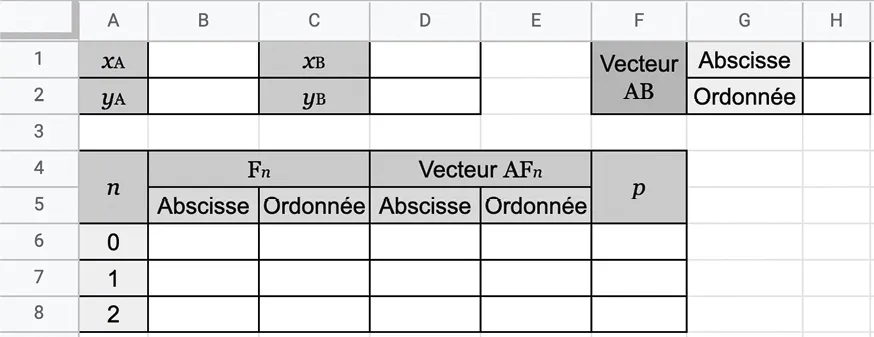
2. Quelles formules doit‑on saisir dans les cellules \bf{H1} et \bf{H2} pour calculer les coordonnées de \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}} ?
3. a. Quelles formules faut‑il saisir et étirer vers le bas dans les cellules \bf{B6} et \bf{C6} pour calculer les coordonnées de \mathrm{F}_{n} ?
b. Quelles formules faut‑il saisir et étirer vers le bas dans les cellules \bf{D6} et \bf{E6} pour calculer les coordonn�ées de \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AF}_{n}} ?
4. Dans la cellule \bf{F6}, saisir la formule \color{purple}\bf{=\$ \mathbf{H} \$ \mathbf{1}^{*} \mathbf{D} \mathbf{6}+\mathbf{\$} \mathbf{H} \mathbf{\$} \mathbf{2}^{*} \mathbf{E} 6}. Que calcule‑t‑elle ? Expliquer les \color{purple}\bf{\$} présents dans la formule.
5. Déterminer la valeur de n telle que le travail soit nul, puis donner les coordonnées de \mathrm{F}_{n} correspondantes.


2. Quelles formules doit‑on saisir dans les cellules \bf{H1} et \bf{H2} pour calculer les coordonnées de \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}} ?
3. a. Quelles formules faut‑il saisir et étirer vers le bas dans les cellules \bf{B6} et \bf{C6} pour calculer les coordonnées de \mathrm{F}_{n} ?
b. Quelles formules faut‑il saisir et étirer vers le bas dans les cellules \bf{D6} et \bf{E6} pour calculer les coordonn�ées de \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AF}_{n}} ?
4. Dans la cellule \bf{F6}, saisir la formule \color{purple}\bf{=\$ \mathbf{H} \$ \mathbf{1}^{*} \mathbf{D} \mathbf{6}+\mathbf{\$} \mathbf{H} \mathbf{\$} \mathbf{2}^{*} \mathbf{E} 6}. Que calcule‑t‑elle ? Expliquer les \color{purple}\bf{\$} présents dans la formule.
5. Déterminer la valeur de n telle que le travail soit nul, puis donner les coordonnées de \mathrm{F}_{n} correspondantes.
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Méthode de résolution 3 GeoGebra
1. Placer les points \text{A} et \text{B}, créer un curseur n variant de 0 à 30 avec un incrément de 1, puis créer le point \mathrm{F}_{n}.
2. Définir les vecteurs u=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}} et v=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AF}_{n}}. Saisir la formule : \color{purple}\bf{\mathbf{p}=\mathbf{x}(\mathbf{u}) \mathbf{x}(\mathbf{v})+\mathbf{y}(\mathbf{u}) \mathbf{y}(\mathbf{v})}.
À quoi correspond \color{purple}\bf{p} dans cet exercice ?
3. a. En faisant varier n, déterminer la valeur de n pour laquelle le travail est nul.
b. Pour quelles coordonnées de \mathrm{F}_{n} le travail de la force \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AF}_{n}} est‑il nul ?
2. Définir les vecteurs u=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}} et v=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AF}_{n}}. Saisir la formule : \color{purple}\bf{\mathbf{p}=\mathbf{x}(\mathbf{u}) \mathbf{x}(\mathbf{v})+\mathbf{y}(\mathbf{u}) \mathbf{y}(\mathbf{v})}.
À quoi correspond \color{purple}\bf{p} dans cet exercice ?
3. a. En faisant varier n, déterminer la valeur de n pour laquelle le travail est nul.
b. Pour quelles coordonnées de \mathrm{F}_{n} le travail de la force \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AF}_{n}} est‑il nul ?
Ressource affichée de l'autre côté.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Faites défiler pour voir la suite.
Concrètement, le travail d'une force sur un déplacement rectiligne correspond à l'énergie qu'elle produit lorsque le point d'application (souvent le centre de gravité du système étudié) se déplace selon un vecteur \overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}.
On peut remarquer que la définition du travail d'une force diffère de la définition usuelle du mot « travail ». Par exemple, le travail d'une force dont le point d'application ne travaille pas est nul (\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}=\overrightarrow{0}).
Mais si on tient sans bouger et à bout de bras un objet, la force qu'on exerce sur cet objet aura un travail nul, bien que nous ressentions un certain épuisement au bout d'un moment.
On peut remarquer que la définition du travail d'une force diffère de la définition usuelle du mot « travail ». Par exemple, le travail d'une force dont le point d'application ne travaille pas est nul (\overrightarrow{\mathrm{AB}}=\overrightarrow{0}).
Mais si on tient sans bouger et à bout de bras un objet, la force qu'on exerce sur cet objet aura un travail nul, bien que nous ressentions un certain épuisement au bout d'un moment.
Une erreur sur la page ? Une idée à proposer ?
Nos manuels sont collaboratifs, n'hésitez pas à nous en faire part.
j'ai une idée !
Oups, une coquille
